Greetings reader, I required an article for a beginner to understand how to apply the BC547 transistor in basic electronic circuits. Since there was no clear and correct tutorial, I have created this basic article describing the working, pinout, specifications, and uses of the transistor in a simple way.
BC547 Transistor Overview
BC547 is an NPN bipolar junction transistor. If the base pin is grounded (shorted to ground), the emitter and collector remain open (reverse-biased), i.e., the transistor is off. When a voltage is supplied to the base, then the transistor becomes forward-biased and current is passed from the collector to the emitter. This makes it more suitable for switching and amplification applications.
BC547 Transistor Pinout Diagram
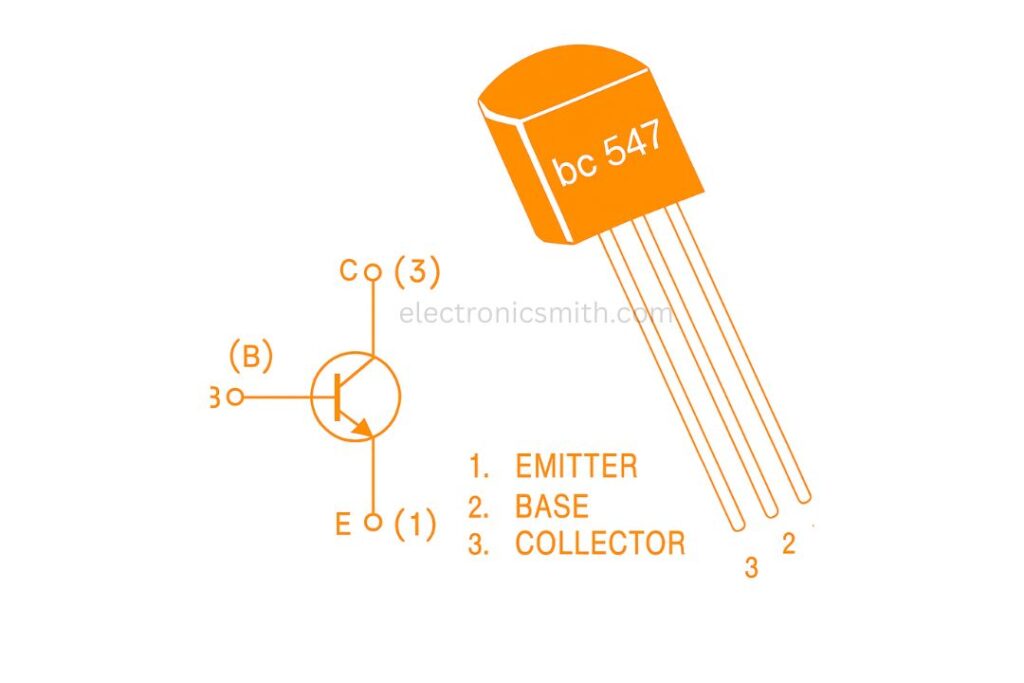
| Pin Number | Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Collector | Current enters through this terminal |
| 2 | Base | Controls the transistor’s operation |
| 3 | Emitter | Current exits through this terminal |
Electrical Characteristics of BC547
Understanding the key parameters of BC547 is essential for choosing it in the correct context.
- Collector-Emitter Voltage (V<sub>CE</sub>): 65V
- Collector-Base Voltage (V<sub>CB</sub>): 80V
- Emitter-Base Voltage (V<sub>EB</sub>): 8V
- Maximum Collector Current (I<sub>C</sub>): 100mA
- DC Current Gain (h<sub>FE</sub>): Up to 800
- Transition Frequency (f<sub>T</sub>): 150 MHz (typical)
- Package Power Dissipation: ~500 mW
Working Principle and Modes of Operation
The BC547 transistor operates based on how it is biased in the circuit, which determines whether it allows current to flow or not. It essentially acts as a switch or amplifier depending on the mode of operation.
Forward Active Mode
In this mode, the base-emitter junction is forward biased while the collector base junction is reverse biased. When a small current flows into the base terminal it allows a much larger current to pass from the collector to the emitter. This makes the transistor behave like an amplifier, where it can boost weak signals. It is the most commonly used mode in analog electronics.
Cut-Off / Reverse Bias Mode
When both the base-emitter and collector base junctions are reverse biased the transistor remains in the cut-off region. In this state no current flows from collector to emitter and the transistor effectively acts like an open switch. This mode is primarily used in digital logic and switching applications, where the transistor either allows or blocks current completely.
Brief Description of BC547
The BC547 transistor has a DC gain of 110 to 800, which is a measure of how effectively it can amplify a signal. The collector current is up to 100mA and, as such, suitable for small loads only. The base current (IB) must be limited to 5mA maximum, commonly controlled by a base resistor.
When the transistor is fully ON (saturated), there is uncontrolled current flow from emitter to collector. In the saturation region, collector-emitter voltage (VCE) is approximately 200mV and base-emitter voltage (VBE) is approximately 900mV.
When the base current is interrupted, the transistor is completely switched OFF. This is what is called the cut-off region, when VBE is close to 660mV and there is no collector current.
BC547 as a Switch
BC547, when used as a switch, is in the region between cut-off (OFF) and saturation (ON).
1. When forward-biased, the transistor acts like a closed switch.
2. In the reverse bias, it is an open switch.
To limit the base current, a resistor is connected in series with the base pin. The formula can obtain the value of the resistor (RB):
RB=VBE/IBWhere:
- VBE ≈ 0.7V (for BC547)
- IB depends on the required collector current (IC)
BC547 as an Amplifier
BC547 is utilized as an amplifier in the active region. It is capable of amplifying:
- Show
- Voltage
- Power
- Common Amplifier Configurations
- Common Emitter Amplifier (most commonly used)
- Common Collector Amplifier
- Common Base Amplifier
To find the DC current gain (hFE) in the above example of an amplifier:
hFE=IC/IBApplications
Relay driver modules
Audio amplifier modules
Signal amplifier circuits
Darlington pairs
General-purpose switching and amplification
Conclusion
In conclusion, the BC547 is a versatile NPN transistor ideal for beginners exploring basic electronics. This article has simplified its working principle, pin configuration, specifications, and practical applications. Whether used as a switch or amplifier, the BC547 is a reliable component for low-power electronic projects, making it a fundamental building block in understanding transistor-based circuits.
